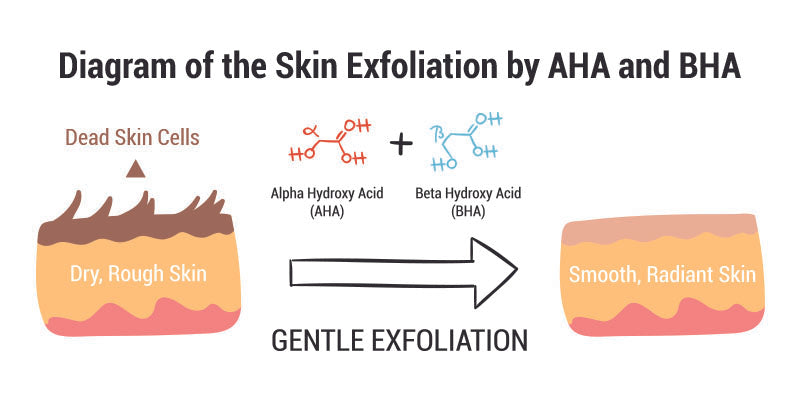
AHA
Acronym for alpha hydroxy acid. AHAs are derived naturally from various plant sources and from milk, but 99% of the AHAs used in cosmetics are syntatically derived. In low concentrations (less than 3%), AHAs work as water-binding agents. At concentrations greater than 4% and in a base with an acid pH of 3 to 4, these ingredients can exfoliate skin cells by breaking down the substance in skin that holds skin cells together.
The most effective and well-researched AHAs are glycolic acid and lactic acid.
AHAs may irritate mucous membranes and cause irritation. However, AHAs have been widely used for therapy of photodamaged skin, and also have been reported to normalize over-thickened skin and to increase viable epidermal thickness and dermal glycosaminoglycans content, all of which lead to younger-looking skin.
There is a vast amount of research that substantially describes how the aging process affects skin and that demonstrates that many of the unwanted changes can be improved by topical application of AHAs, including glycolic and lactic acids. Because AHAs exfoliate sun-damaged cells from the surfaceof skin, and because this layer imparts some minimal sun protection for skin, there is a risk of increased sun sensitivity when using an AHA. However, wearing a sunscreen daily eliminates this risk.